Docker Desktop - Zero to Hero
This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough for setting up and utilizing Docker Desktop on Windows and macOS systems. It details specific hardware requirements, such as virtualization support and memory needs, alongside step-by-step instructions for graphical and command-line installations.
Beyond setup, the text explains how containers function as isolated environments that share the host’s kernel while remaining portable and efficient. Essential concepts like volume mounting for data persistence and port mapping for network access are highlighted to show how containers interact with the host machine. Users can manage these processes through either a web-based interface or a visual dashboard to monitor performance and logs. Overall, the source serves as a practical roadmap for developers to transition from initial installation to running their first containerized applications.
Listen to the NotebookLM podcast before or while you’re reading this post.
Installing Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop is the easiest way to run containers locally on both macOS and Windows, and the installation is mostly a point-and-click process on each platform. This tutorial walks through prerequisites, installation, and basic verification for both operating systems so you can be ready to run your first container.1

Docker Desktop bundles everything you need for local container development.1
- Docker Engine and Docker CLI to build and run containers.1
- Docker Compose v2 for multi-container apps.1
- A graphical dashboard to manage containers, images, and volumes.1
- Integration with WSL 2 on Windows and native virtualization on macOS.23
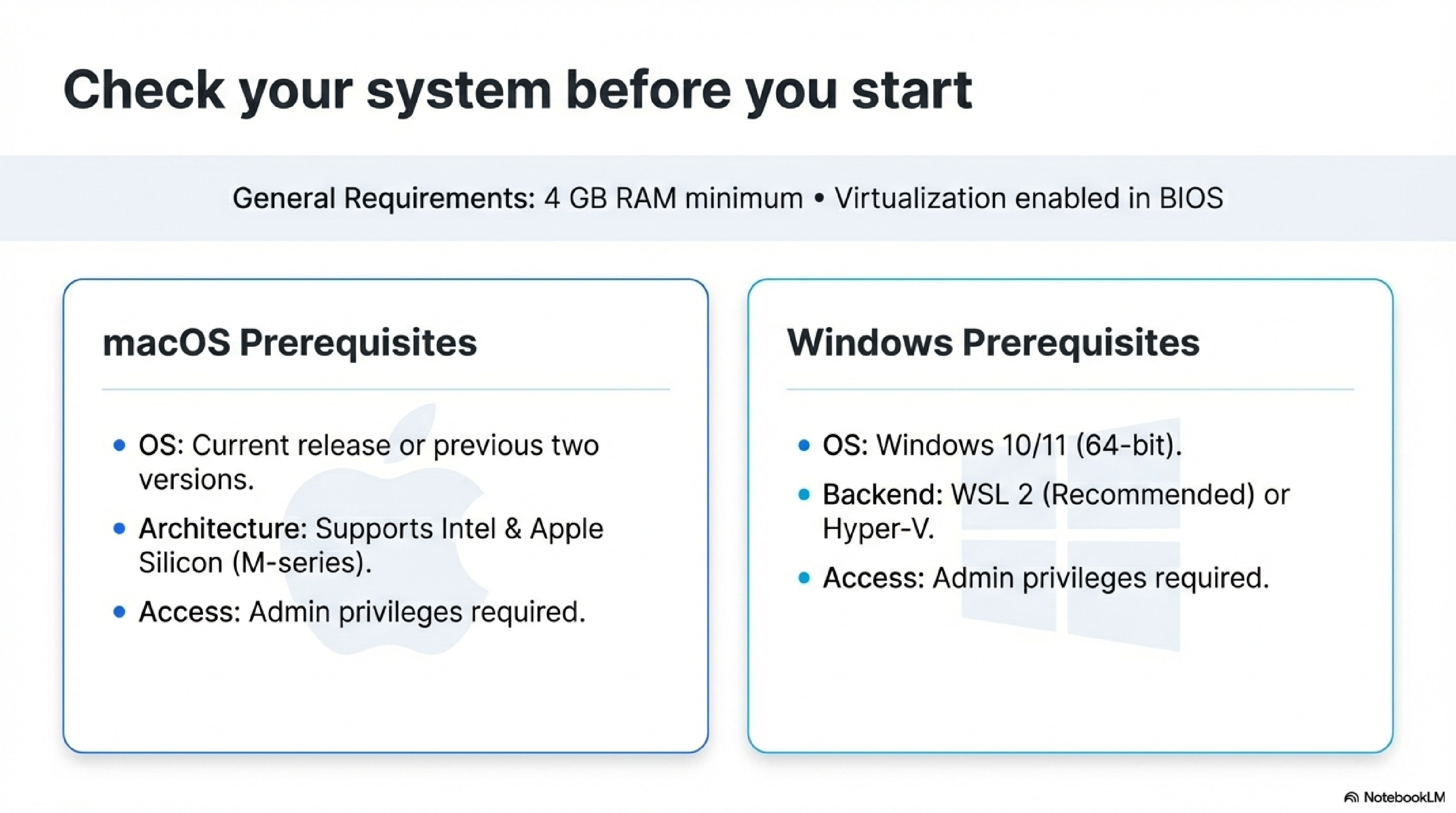
Before installing, confirm that your machine meets the minimum requirements.32
- RAM: At least 4 GB.42
- Virtualization: Enabled in BIOS/firmware (Windows) or supported by your Mac’s CPU (Intel or Apple Silicon).23
For macOS:2
- Supported macOS: current release and previous two major versions.52
- 4 GB RAM or more, admin access to install apps.2
- 64‑bit Windows 10 or 11, latest updates recommended.45
- Hardware virtualization enabled, WSL 2 or Hyper‑V available depending on edition.53
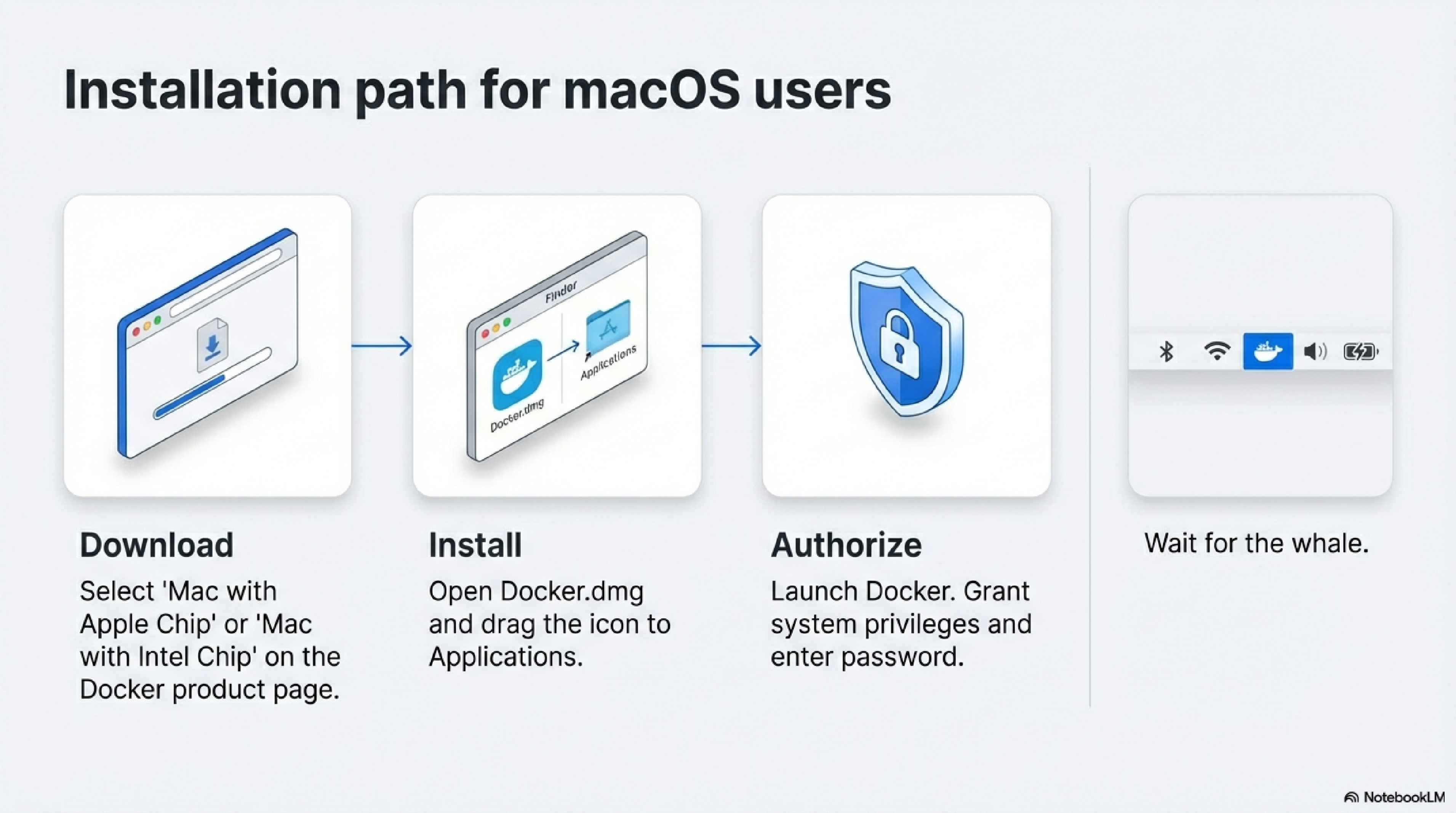
These steps cover the standard GUI installation on Mac.62
- Download Docker Desktop for Mac
- Go to the Docker Desktop https://docs.docker.com/desktop/ product page and choose the Mac download that matches your chip (Apple Silicon or Intel).76
- Save the
Docker.dmgfile to your Downloads folder.6
- Run the installer
- First launch and permissions
- Optional: Install via command line
- Verify your installation
- Wait for the Docker whale icon to appear in the macOS menu bar and show “Docker Desktop is running.”8
- Open Terminal and run:
docker version docker run hello-world - You should see Docker client/server version output and a short message from the
hello-worldcontainer confirming that Docker works correctly.2
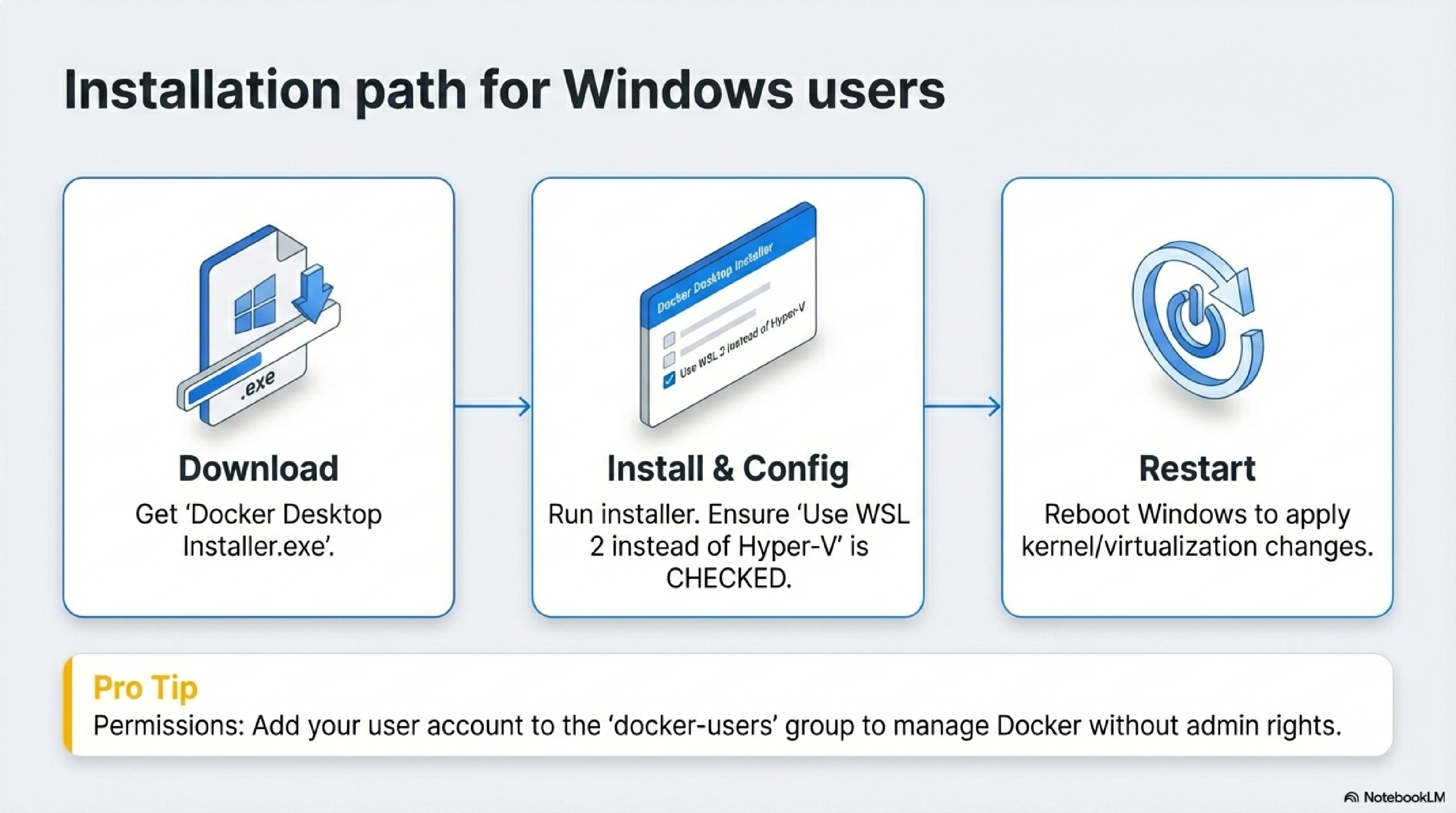
On Windows, Docker Desktop integrates with WSL 2 or Hyper‑V; the interactive installer handles most configuration.34
Download Docker Desktop for Windows
Run the installer
- Double‑click
Docker Desktop Installer.exeto start installation.34 - If prompted, allow the app to make changes (you may need to run as Administrator).94
- In the configuration screen, you can choose options such as “Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper‑V,” enabling WSL 2 integration if supported.93
- Docker Desktop installs by default to
C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker.103
- Double‑click
Command-line installation (optional)
- After downloading the installer, you can script installation, for example from PowerShell:43
"Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install - From PowerShell with explicit start:
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait install - From Command Prompt:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install - This is useful for automated setups or lab environments.34
- After downloading the installer, you can script installation, for example from PowerShell:43
Post-install configuration
- When installation completes, you may be prompted to restart Windows; accept the restart so kernel and virtualization changes apply.9
- If your admin account differs from your user account, add your user to the
docker-usersgroup so you can manage Docker components:43net localgroup docker-users <user> /add
Verify your installation
- Launch Docker Desktop from the Start menu and wait until the status indicates that Docker is running.93
- Open PowerShell or Command Prompt and run:
docker version docker run hello-world - As on macOS, you should see a confirmation message from the
hello-worldcontainer if everything is configured correctly.34
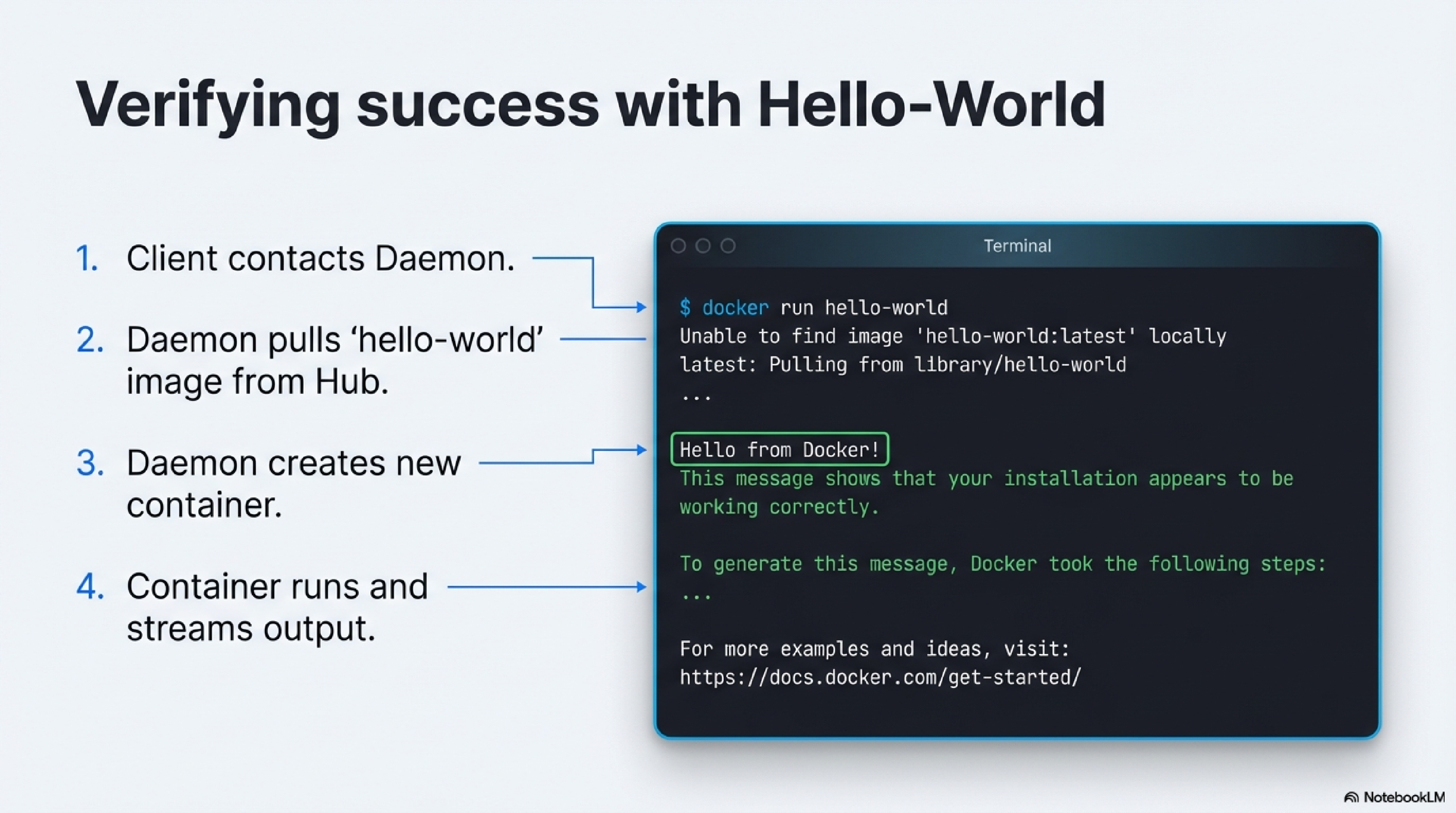
- Pull a public image:
docker pull nginx - Run a container in the background:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginx - Open Docker Desktop’s GUI to inspect running containers, view logs, and stop or remove containers from the dashboard.1
This flow—download, install, verify with hello-world, then run a simple web server—gives readers a complete end‑to‑end path for getting Docker Desktop working on both macOS and Windows.
Docker Containers at a High Level
Docker containers provide lightweight, isolated environments for running applications by packaging code with its dependencies, sharing the host’s OS kernel for efficiency. They connect to the host via filesystem volumes and port mappings, allowing seamless data access and network communication without needing a full virtual machine.16171819
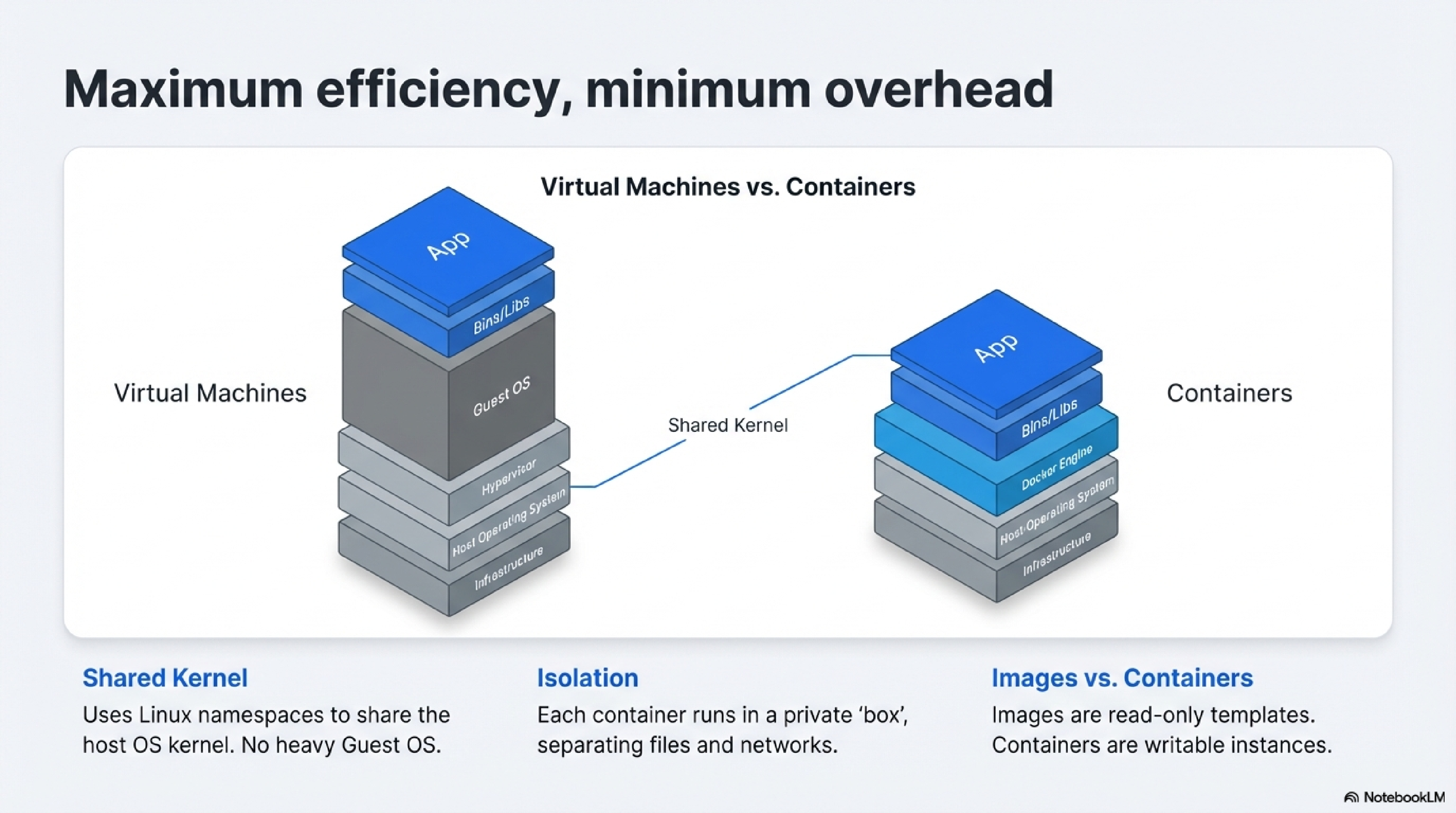
Containers work by using Linux kernel features like namespaces and cgroups to isolate processes, filesystems, networks, and resources from the host.1820
- Each container runs a single process or app in its own isolated “box,” but multiple containers share the host kernel for low overhead (unlike VMs).1721
- Images are read-only templates (layers of filesystems); containers are writable instances of those images.18
- They start in seconds and ensure apps run identically across development, testing, and production.2016
Containers lack native GUI support, as they focus on headless services rather than desktop apps with graphical interfaces.18
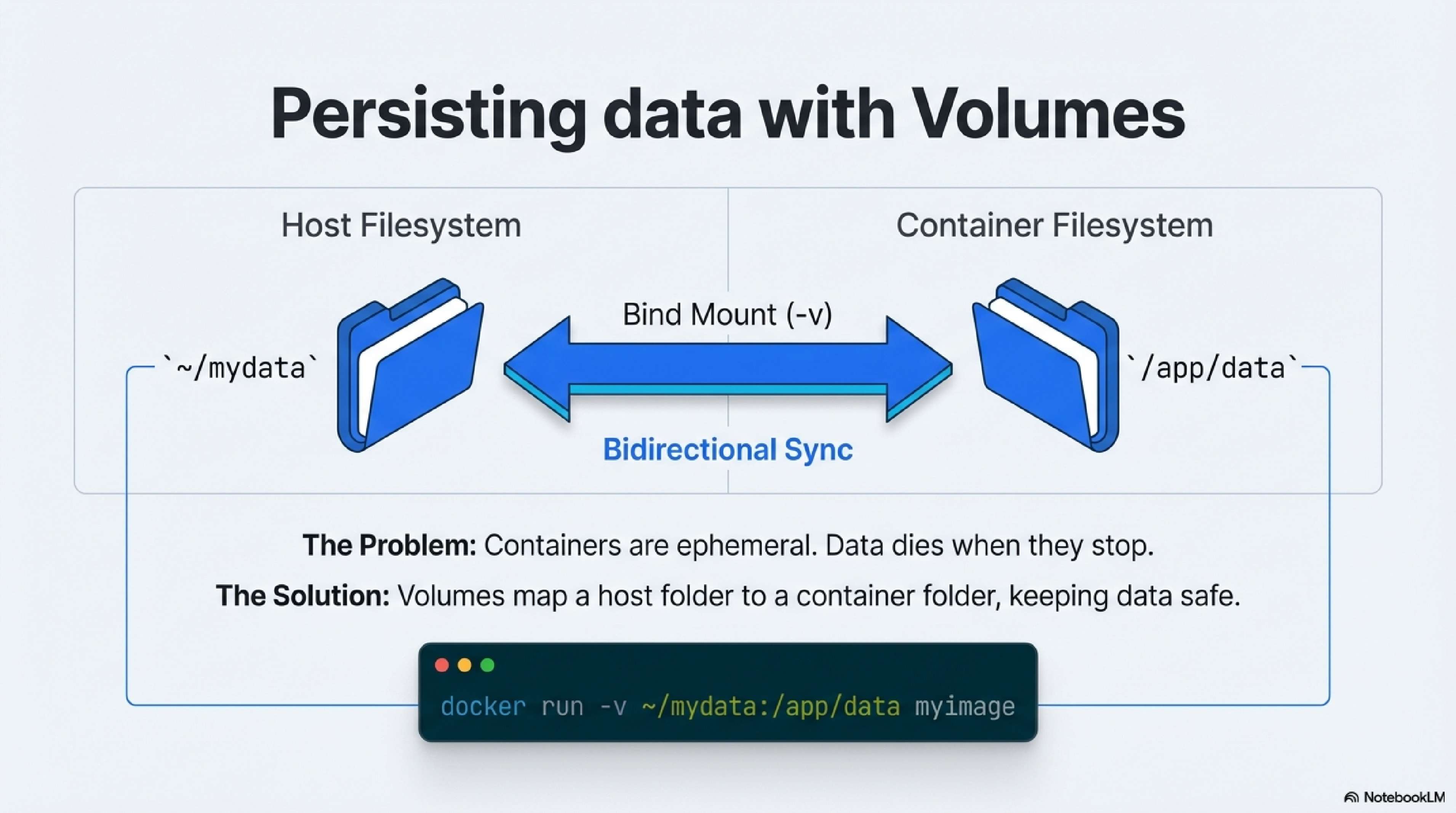
Containers access host data through volumes or bind mounts, which map host directories to paths inside the container.2223
- Use
-v /host/path:/container/pathindocker runto share files bidirectionally; changes on either side sync immediately.2322 - This lets containerized apps read, write, or manipulate host data files like any local program—for example, mounting a data folder for a database container.23
- Volumes persist data beyond container lifecycles, preventing loss when containers stop or delete.22
Example: docker run -v ~/mydata:/app/data myimage lets the app inside treat /app/data as local storage.
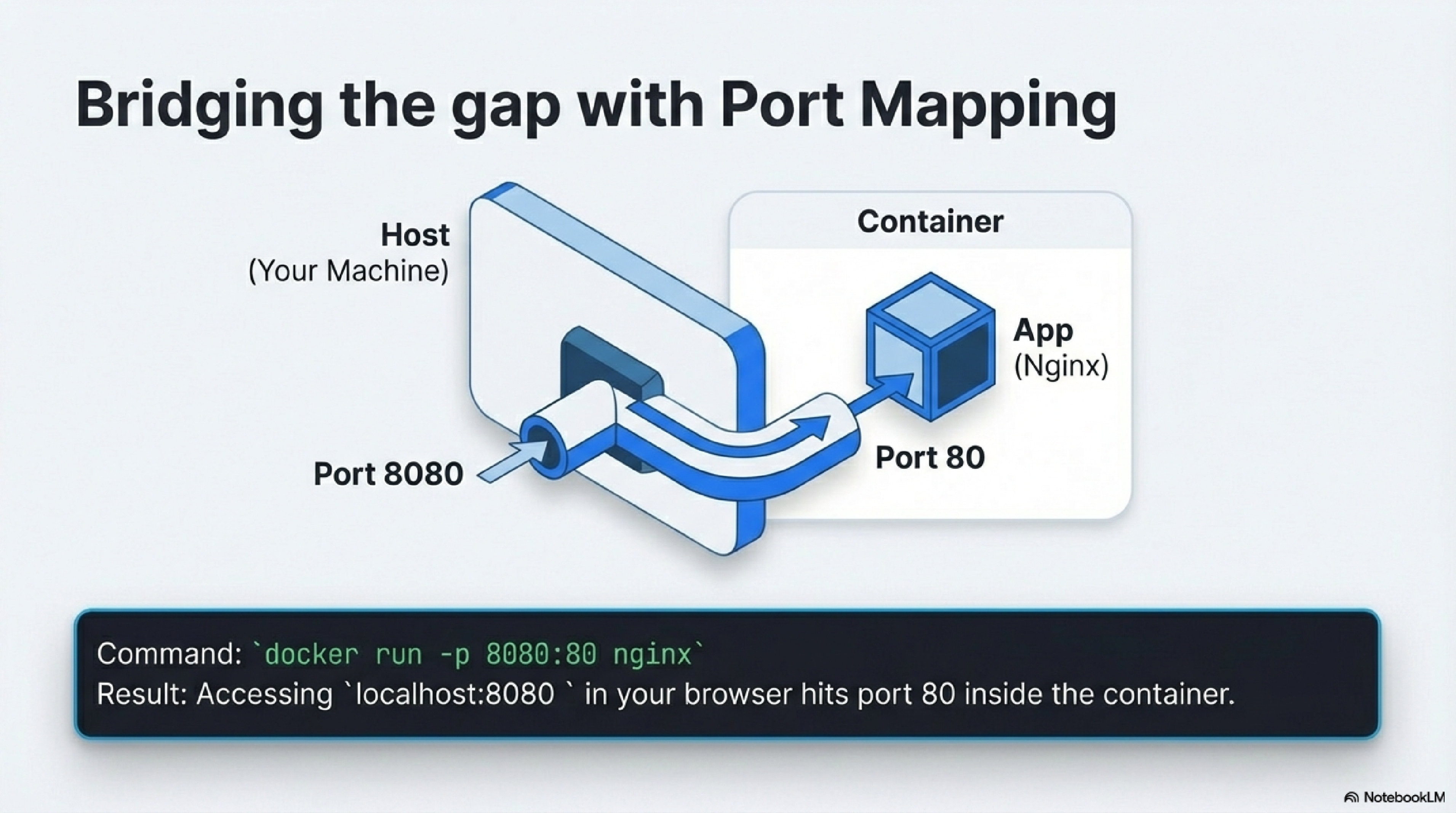
A server is software that listens for incoming connections on a port (a numbered endpoint, like 80 for HTTP or 5432 for PostgreSQL).1924
- Containers have private networks by default; port mapping (
-p host_port:container_port) forwards host traffic to the container via NAT.2519 - Example:
-p 8080:80maps your machine’s port 8080 to the container’s 80, solocalhost:8080reaches the app inside.2419 - Containers communicate with the host or each other like remote servers over these ports.26
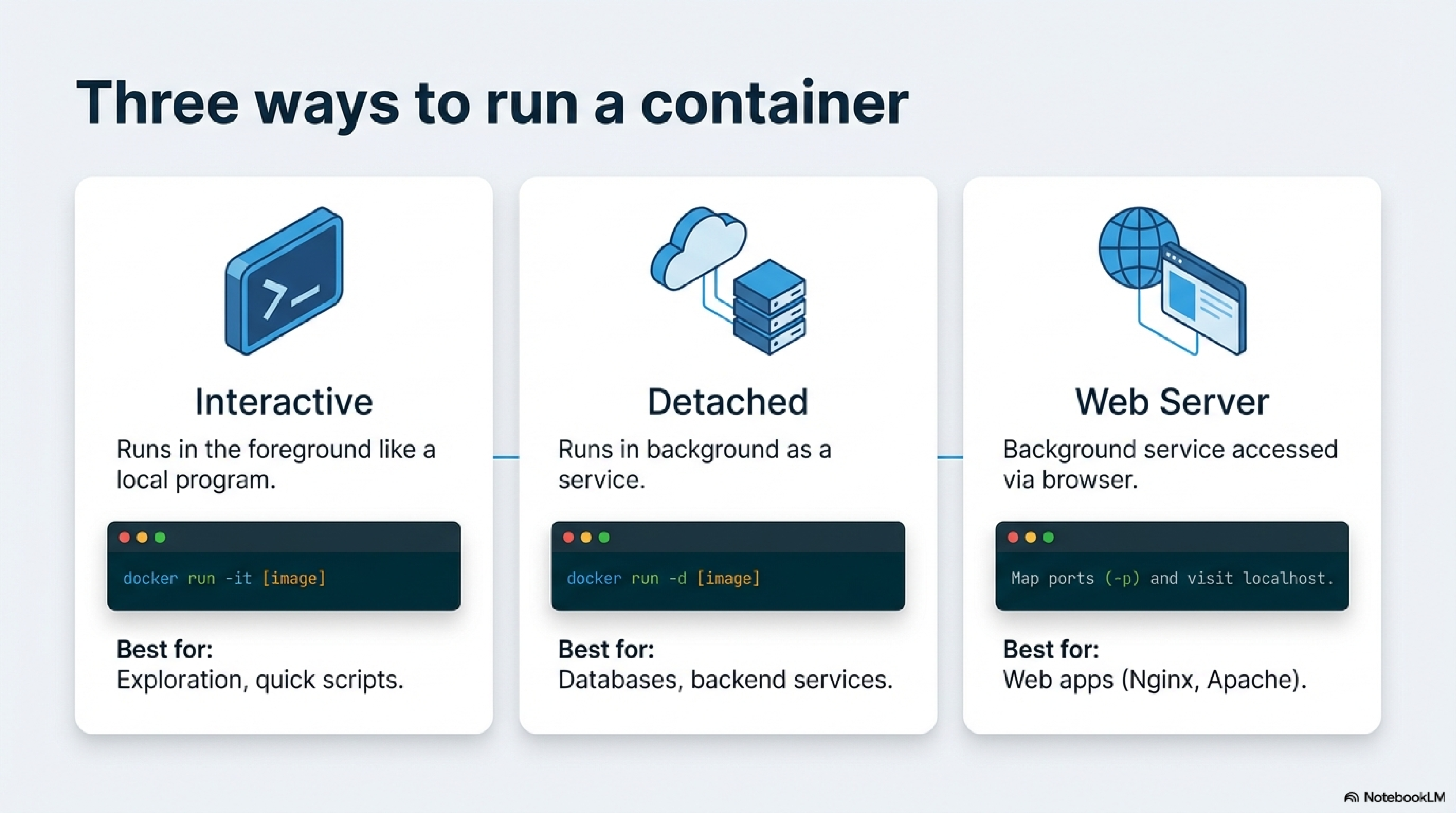
- Foreground CLI mode: Run interactively like a local program (e.g.,
docker run -it -v /host/data:/data mydb psql). Access via terminal, manipulating host files directly.23 - Remote server connection: Run detached (
-d), connect via CLI tools (e.g.,docker exec -it container psql)—behaves like SSH to a remote service.27 - Background web server: Map ports and access via browser (e.g.,
docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginx). Users hitlocalhost:8080to interact with the web app.1924

Docker Desktop’s dashboard offers a visual interface to monitor and control all containers without CLI commands.2827
| Action | How to Do It in Dashboard | What It Shows/Does |
|---|---|---|
| View list | Containers tab lists running/stopped ones; search by name. | Status, CPU/memory usage, uptime.27 |
| Start/Stop/Restart | Select container → buttons for play/pause/stop/restart. | Real-time stats and quick actions.27 |
| Inspect details | Click container → tabs for Logs, Inspect, Bind mounts, Stats, Files. | Resource graphs, volumes, env vars, exec console.27 |
| Open ports/apps | Click “Open in Browser” for mapped ports or “Open in VS Code.” | Direct browser access; editor integration.27 |
| Delete/Copy command | Delete button or copy docker run snippet for reuse. | Cleanup and scripting aid.27 |
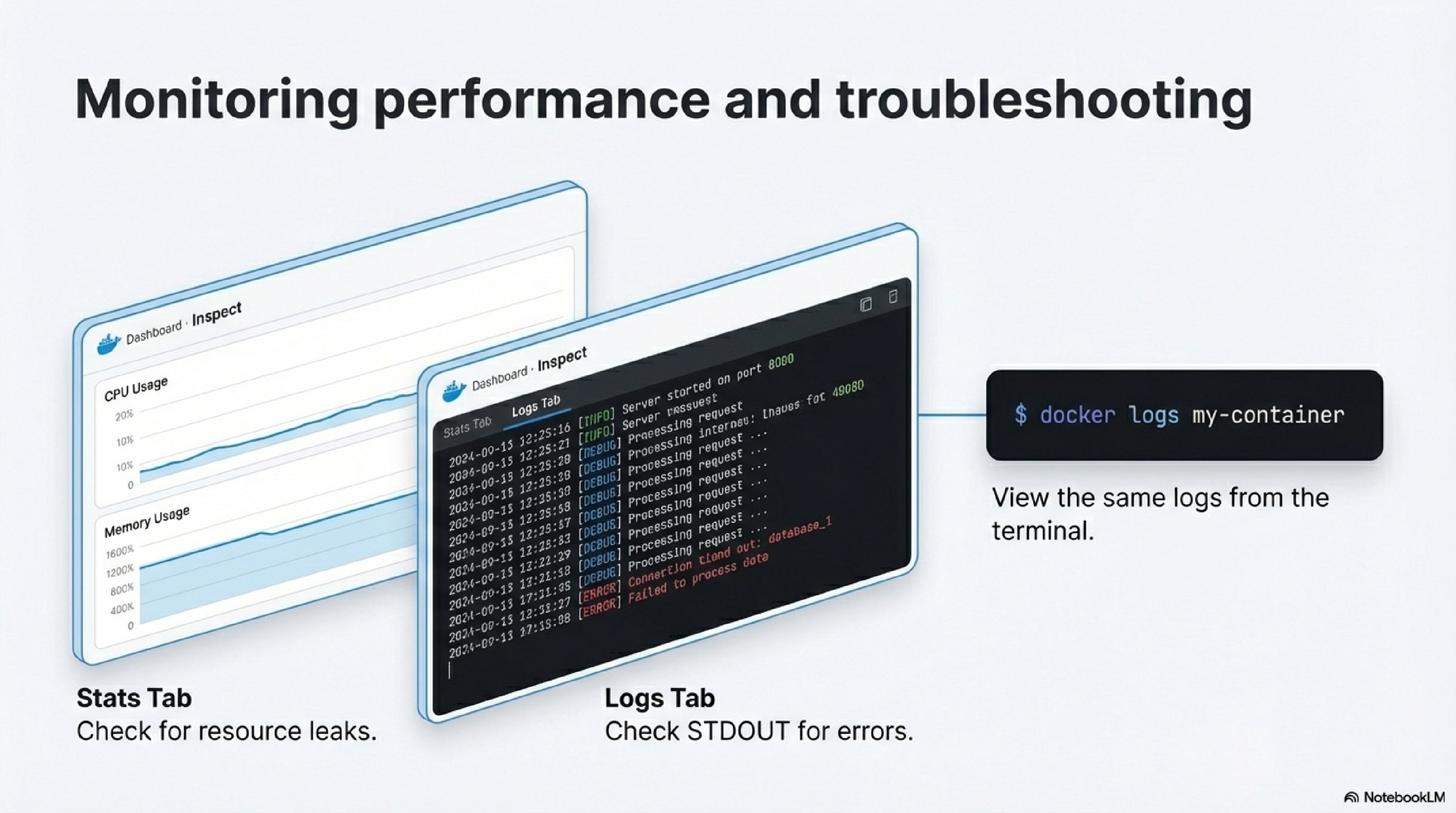
Use the Stats tab for live CPU/memory/network graphs and Logs for troubleshooting output.2827

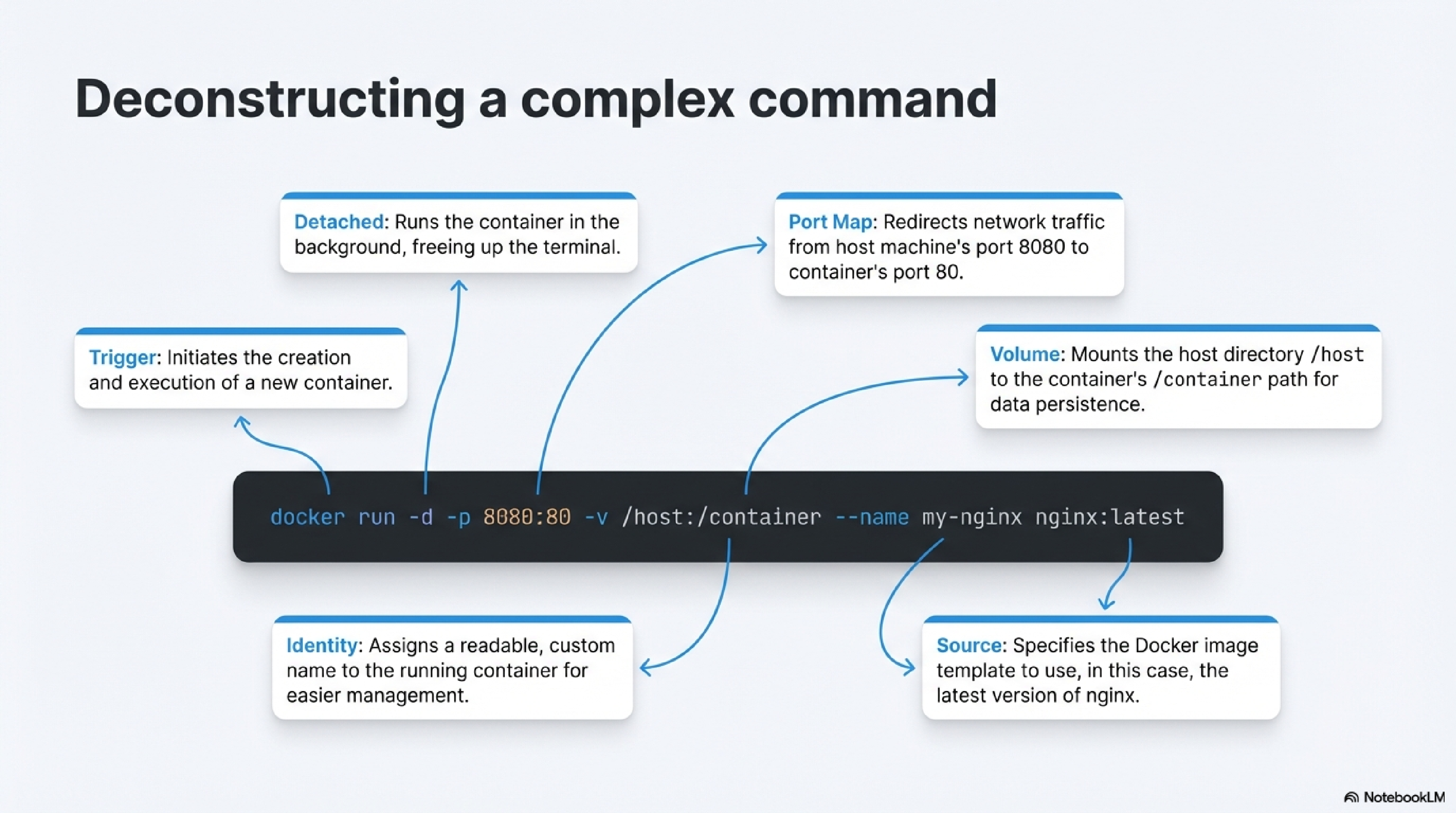
Here’s a simple example that does both port mapping and a volume mount:
docker run -d \
-p 8080:80 \
-v /path/on/host:/usr/share/nginx/html \
--name my-nginx \
nginx:latest
-druns the container in the background (detached).-p 8080:80maps port 8080 on your host to port 80 inside the container.-v /path/on/host:/usr/share/nginx/htmlmounts a host directory into the container.--name my-nginxgives the container a readable name.nginx:latestis the image being run.
References
https://docs.docker.com/desktop/setup/install/mac-install/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://docs.docker.com/desktop/setup/install/windows-install/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/docker-tutorial/install-docker-on-windows ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://sites.northwestern.edu/spsit/instructions/minimum-system-requirements-for-docker/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://dev.to/meghasharmaaaa/install-docker-desktop-on-mac-465d ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/introduction/get-docker-desktop/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://docs.demonwarriortech.com/Documented Tutorials/Docker/Docker_Desktop_Install_on_Windows/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://dev.to/meghasharmaaaa/install-docker-desktop-on-windows-31ni ↩︎
https://github.com/WCSCourses/index/blob/main/Docker_guide.md ↩︎
https://forums.docker.com/t/good-requirements-for-docker-desktop-on-macosventura/134101 ↩︎
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/openpages/9.0.0?topic=docker-installing ↩︎
https://wiki.mdriven.net/Documentation:Deployment:_Two_Ways_To_Install_Docker_Desktop_on_MacOS_Intel ↩︎
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/install-docker.html ↩︎
https://oneuptime.com/blog/post/2025-12-08-how-docker-actually-works/view ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://docs.docker.com/engine/network/port-publishing/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-docker-containers-work/ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.reddit.com/r/docker/comments/keq9el/please_someone_explain_docker_to_me_like_i_am_an/ ↩︎
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40905761/how-do-i-mount-a-host-directory-as-a-volume-in-docker-compose ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-share-data-between-the-docker-container-and-the-host ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://iamachs.com/blog/docker/part-4-networking-fundamentals-for-containers/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.aquasec.com/cloud-native-academy/docker-container/docker-networking/ ↩︎
https://dev.to/vinothmohan/docker-an-overview-at-high-level-21jk ↩︎
https://docs.docker.com/desktop/use-desktop/container/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://grafana.com/blog/easily-monitor-docker-desktop-containers-with-grafana-cloud/ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://docs.docker.com/reference/cli/docker/container/run/ ↩︎
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19335444/how-do-i-assign-a-port-mapping-to-an-existing-docker-container ↩︎
https://www.baeldung.com/ops/assign-port-docker-container ↩︎